In 2009, two entrepreneurs faced a common problem in San Francisco: the struggle to find affordable accommodation during a design conference. Their solution? Offering air mattresses in their living room to conference attendees. This simple idea evolved into Airbnb, revolutionizing the hospitality industry and creating a platform now valued at over $75 billion. Their success wasn’t just about the idea—their innovative business model transformed how people think about travel accommodation.
At its core, a business model is the blueprint that defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s the fundamental architecture of your business operations, revenue streams, and customer relationships. For startups, having the right business model isn’t just important—it’s the difference between thriving and joining the 90% of startups that fail within their first year.
Today’s digital landscape offers entrepreneurs various proven business models to consider. Three dominant approaches stand out: Business-to-Business (B2B), where companies sell products or services to other businesses; Business-to-Consumer (B2C), focusing on direct sales to individual customers; and Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), enabling peer-to-peer transactions. Each model presents unique opportunities and challenges, and understanding their nuances is crucial for entrepreneurs looking to build sustainable businesses in a competitive marketplace.
Table of Contents
 B2B Business Model
B2B Business Model
The Business-to-Business (B2B) model is a cornerstone of modern commerce. At its essence, B2B involves companies selling products, services, or solutions directly to other businesses rather than individual consumers. This model powers everything from corporate operations software to the raw materials that fuel manufacturing processes.
 Core Concept and Operation
Core Concept and Operation
B2B transactions form the backbone of the supply chain, creating a complex web of business relationships that ultimately enable the delivery of products and services to end consumers. These interactions typically involve:
- Multiple stakeholders in the decision-making process
- Customized solutions and pricing structures
- Ongoing service relationships and support systems
- Integration of products/services into the client’s business operations
 Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics
Long-term Relationship Focus
Unlike consumer-focused models, B2B businesses invest heavily in relationship building. This involves:
- Dedicated account managers for key clients
- Regular business reviews and strategic planning sessions
- Customized service level agreements (SLAs)
- Collaborative product development and feedback loops
Complex Sales Cycles
The B2B sales process typically involves:
- Multiple touchpoints across different departments
- Detailed technical discussions and requirements gathering
- ROI analysis and business case development
- Contract negotiations and legal reviews
- Implementation planning and change management
Value Proposition Emphasis
Successful B2B companies excel at:
- Demonstrating clear return on investment
- Addressing specific business pain points
- Providing comprehensive solutions rather than standalone products
- Offering scalable solutions that grow with their clients
 Real-World Examples
Real-World Examples
SaaS Companies
- Salesforce: Provides cloud-based CRM solutions
- SAP: Offers enterprise resource planning systems
- HubSpot: Delivers integrated marketing and sales platforms
Consulting Firms
- McKinsey & Company: Strategic business consulting
- Deloitte: Professional services and advisory
- Accenture: Technology and business transformation services
Wholesale Suppliers
- Cisco: Network equipment and solutions
- Intel: Semiconductor components
- Grainger: Industrial supplies and equipment
 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Higher Transaction Values
- Average deal sizes typically range from thousands to millions
- More substantial profit margins per transaction
- Greater potential for upselling and cross-selling
- Stable Revenue Streams
- Recurring revenue models through subscriptions or contracts
- More predictable cash flow forecasting
- Higher customer lifetime value
- Strategic Partnerships
- Opportunity for co-development initiatives
- Access to client’s industry expertise
- Mutual growth opportunities
Disadvantages
- Extended Sales Cycles
- Average sales cycles of 3-12 months
- Higher cost of customer acquisition
- Resource-intensive sales process
- Complex Customer Acquisition
- Need for specialized sales expertise
- Multiple decision-makers involved
- Extensive proposal and documentation requirements
- Client Concentration Risk
- Dependence on key accounts
- Vulnerability to client business changes
- Higher impact of client loss
In our digital transformation era, B2B models continue to evolve, incorporating digital commerce, automation, and artificial intelligence elements. Success in this space requires not just superior products or services but also a deep understanding of client needs, strong relationship management capabilities, and the ability to consistently deliver measurable business value.
Do You Have a Destination In Mind
Launchroad can help you find the perfect country for your startup. Schedule a free demo today.
 B2C Business Model
B2C Business Model
Business-to-consumer (B2C) commerce is the most familiar face of commerce, where companies sell products or services directly to individual consumers. From your morning coffee purchase to streaming your favorite show, B2C transactions form the fabric of daily consumer life. This model has evolved dramatically in the digital age, transforming from traditional brick-and-mortar operations to sophisticated omnichannel experiences.
 Core Concept and Operation
Core Concept and Operation
The B2C model focuses on creating direct relationships between businesses and individual consumers. Success in this space relies on the following:
- Understanding and meeting consumer needs effectively
- Creating seamless purchase experiences
- Building strong brand recognition
- Maintaining competitive pricing
- Delivering consistent value to end users
 Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics
Consumer-Centric Focus
B2C businesses thrive on understanding and catering to individual preferences:
- Personalized shopping experiences
- Intuitive user interfaces
- Convenient payment options
- Responsive customer service
- Easy returns and exchanges
Streamlined Sales Process
The B2C purchase journey typically involves:
- Quick decision-making cycles
- Minimal negotiation
- Immediate gratification
- Simple pricing structures
- Easy-to-understand product offerings
Marketing and Brand Experience
Success factors include:
- Strong brand identity and recognition
- Emotional connection with customers
- Engaging social media presence
- Targeted advertising campaigns
- Loyalty programs and rewards
 Real-World Examples
Real-World Examples
E-commerce Platforms
- Amazon: Global marketplace with rapid delivery
- ASOS: Fashion-focused online retail
- Wayfair: Home goods and furniture
Retail Chains
- Target: Multi-category department stores
- Starbucks: Coffee and beverage retail
- H&M: Fast fashion retail
Subscription Services
- Netflix: Streaming entertainment
- HelloFresh: Meal kit delivery
- Birchbox: Beauty product subscriptions
 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Expansive Market Potential
- Access to millions of potential customers
- Geographic scalability
- Multiple market segment opportunities
- Viral marketing potential
- Rapid Sales Cycles
- Quick purchase decisions
- Immediate transactions
- Faster inventory turnover
- Real-time market feedback
- Simplified Customer Acquisition
- Direct marketing channels
- Clear value propositions
- Straightforward onboarding
- Multiple acquisition channels
Disadvantages
- Lower Transaction Values
- Smaller average order sizes
- Price sensitivity
- Frequent discounting pressure
- Thin profit margins
- High Customer Acquisition Costs
- Competitive advertising landscape
- Rising digital marketing costs
- Need for continuous promotion
- Customer loyalty challenges
- Market Saturation
- Intense competition
- Low barriers to entry
- Price wars
- Rapid market changes
Evolution and Innovation
Today’s B2C landscape continues to evolve with:
- AI-powered personalization
- Augmented reality shopping experiences
- Voice commerce integration
- Social commerce platforms
- Sustainable and ethical business practices
The most successful B2C businesses excel at creating memorable customer experiences while maintaining operational efficiency. They understand that in today’s market, success isn’t just about the product—it’s about the entire customer journey, from discovery to post-purchase support.
Key to thriving in the B2C space is the ability to:
- Adapt quickly to changing consumer preferences
- Leverage data for personalization
- Maintain competitive pricing while preserving margins
- Build and nurture customer loyalty
- Create seamless omnichannel experiences
As technology advances and consumer expectations evolve, B2C businesses must stay agile and innovative while maintaining focus on their core mission: serving individual consumers effectively and profitably.
📌 Must Read: What is a business plan & why do we need it? 👈
Do You Have a Destination In Mind
Launchroad can help you find the perfect country for your startup. Schedule a free demo today.
 C2C Business Model
C2C Business Model
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) represents the democratization of commerce, enabling individuals to trade directly with each other through digital platforms. This revolutionary model, exemplified by platforms like eBay and Airbnb, has transformed ordinary consumers into micro-entrepreneurs, creating entirely new economic opportunities and reshaping traditional markets.
 Core Concept and Operation
Core Concept and Operation
The C2C model creates digital marketplaces where individuals can interact and transact directly, with the platform serving as an intermediary that:
- Provides the technological infrastructure
- Ensures transaction security
- Establishes trust mechanisms
- Handles payment processing
- Mediates disputes
- Maintains community standards
 Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics
Peer-to-Peer Facilitation
The success of C2C platforms depends on:
- User-friendly interfaces
- Robust search and discovery features
- Clear communication channels
- Rating and review systems
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
Technology Infrastructure
Essential platform components include:
- Secure payment gateways
- User verification systems
- Real-time messaging
- Mobile Accessibility
- Data analytics capabilities
Trust and Community Building
Critical elements for success:
- Verified user profiles
- Transparent review systems
- Community Guidelines
- Safety protocols
- User protection policies
 Real-World Examples
Real-World Examples
Online Marketplaces
- eBay
- Global auction and fixed-price marketplace
- Diverse product categories
- Buyer protection programs
- Etsy
- Handmade and vintage items
- Direct artist-to-consumer sales
- Creative community focus
- Facebook Marketplace
- Local buying and selling
- Social network integration
- Zero listing fees
Peer-to-Peer Lending
- Prosper
- Personal loans between individuals
- Risk-based interest rates
- Automated matching systems
- LendingClub
- Alternative financing options
- Investment opportunities
- Credit assessment tools
Sharing Economy Platforms
- Airbnb
- Home sharing and experiences
- Global reach
- Host and guest verification
- BlaBlaCar
- Long-distance ridesharing
- Cost-sharing model
- Community-based trust
 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Market Potential
- Global user base
- Diverse product/service offerings
- Network effect benefits
- Scalability opportunities
- Operational Efficiency
- Low infrastructure costs
- Automated processes
- Minimal inventory requirements
- Digital-first operations
- Innovation Opportunities
- New market creation
- Niche community development
- Technology integration
- Sustainable consumption models
Disadvantages
- Regulatory Challenges
- Complex legal frameworks
- Cross-border regulations
- Tax compliance issues
- Consumer protection requirements
- Trust and Security
- Fraud prevention needs
- Identity verification challenges
- Payment security concerns
- Quality control issues
- User Experience Management
- Inconsistent service quality
- Customer support complexity
- Dispute resolution challenges
- Platform reliability requirements
Future Trends and Evolution
The C2C landscape continues to evolve with:
- Blockchain integration for security
- AI-powered matching algorithms
- Enhanced verification systems
- Specialized niche marketplaces
- Cross-platform integration
Success in the C2C space requires:
- Strong trust-building mechanisms
- Efficient user experience design
- Robust security measures
- Active community management
- Continuous platform innovation
The future of C2C commerce lies in:
- Enhanced user verification
- Improved fraud prevention
- Seamless payment solutions
- Greater market specialization
- Stronger community features
This model represents a fundamental shift in how individuals interact economically, creating opportunities for peer-to-peer commerce while challenging traditional business structures.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
The evolution of business models from traditional B2B to innovative C2C platforms reflects the dynamic nature of modern commerce. Each model offers unique advantages and challenges, catering to different market needs and business objectives. Whether you’re considering a stable B2B venture, a scalable B2C operation, or a revolutionary C2C platform, success depends on understanding your model’s core characteristics and adapting to market demands.
As technology continues to advance, these models will likely become increasingly interconnected, creating new opportunities for entrepreneurs who can effectively navigate their complexities.
Role of Launchroad in The Seccess of Your Startup Visa

LaunchRoad is your trusted partner for starting a business abroad. We guide you in choosing the right country, understanding visa requirements, and getting your startup off the ground. As an experienced startup visa consultant, we offer expert startup visa consultation to help you navigate the complexities of international expansion. Our team provides the support, mentorship, and resources you need to succeed in the global market.
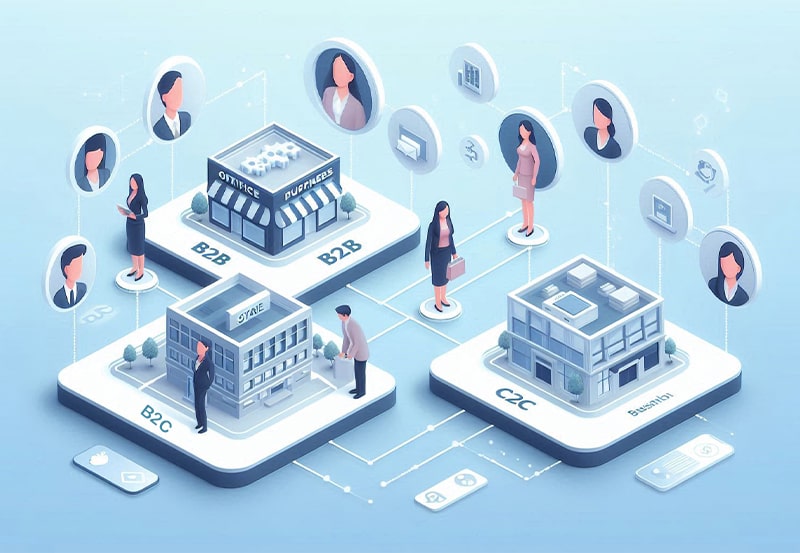

 B2B Business Model
B2B Business Model Core Concept and Operation
Core Concept and Operation Key Characteristics
Key Characteristics Real-World Examples
Real-World Examples Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages and Disadvantages B2C Business Model
B2C Business Model C2C Business Model
C2C Business Model Conclusion
Conclusion









It has no analogues?
It agree, very good information
This rather valuable message
You are not right. I am assured. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM.
Not in it an essence.
The matchless phrase, is pleasant to me 🙂
Great post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed!
Very useful information specifically the last part 🙂
I care for such infolrmation much. I was seeking this certain informattion for a
long time. Thank you and good luck.